MCC Therapeutics is advancing the discovery of a novel, synergistic increase of airways mucociliary clearance by a combination of beta-adrenergic and cholinergic agonists.
MCC Therapeutics is advancing the discovery of a novel, synergistic increase of airways mucociliary clearance by a combination of beta-adrenergic and cholinergic agonists.
Technology
Technology
In most airway diseases, such as in cystic fibrosis, bronchiectasis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma, patients encounter difficulties with airway mucus clearance.
Mucus clearance is critical to keep the airways free of debris and infection.
Mucociliary clearance (MCC) involves multiple mechanisms controlling the production of mucus in the airways and mobilizing it upward and out from the airways.
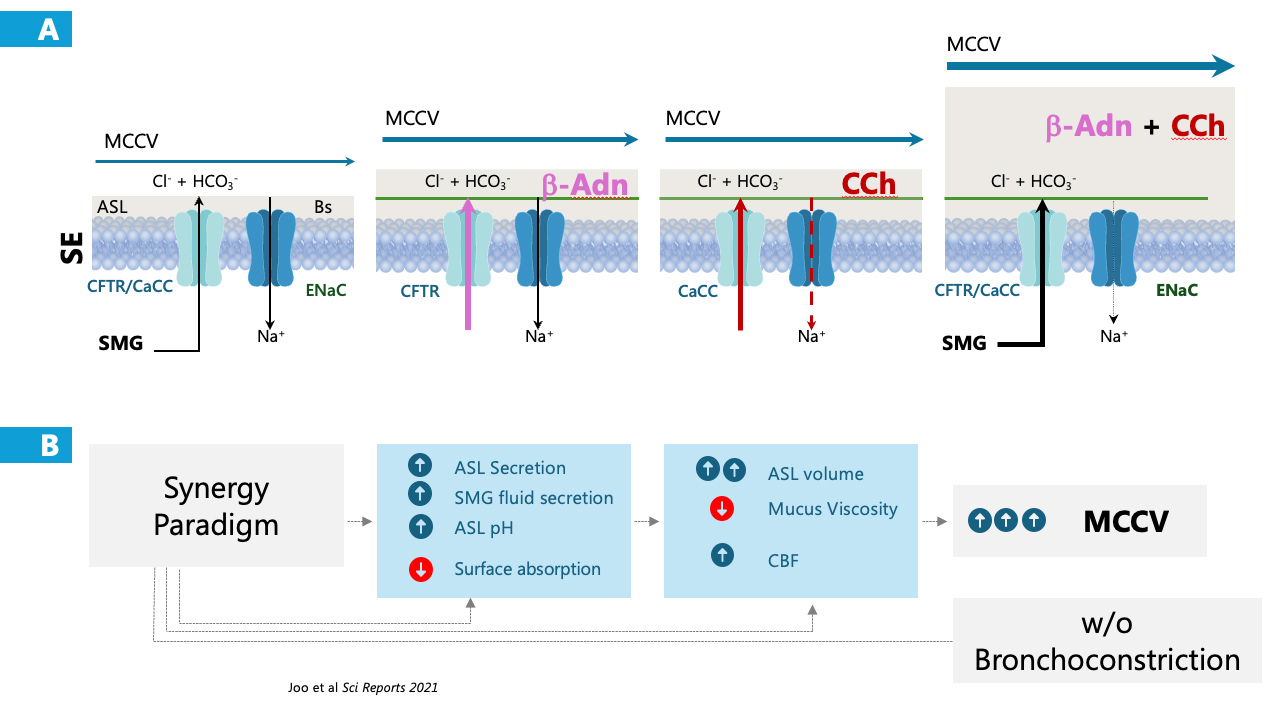
MCC to clear the airways from inhaled debris requires balanced relationship between mucus quantity and viscosity, proper ciliary beat frequency and enough airway surface liquid. These functions are coordinated by the airway epithelium and greatly enhanced by the synergy paradigm.
Drug
Drug
MCCSA2- Inhaled Formoterol Fumarate and Methacholine Chloride
Alone, formoterol is commonly used in airway diseases as a bronchodilator.
Alone, methacholine results in bronchoconstriction which is not seen with the proposed combination.
The combination, MCCSA2, results in increased ASL secretion and decreased absorption, improved ciliary beat velocity without airway narrowing.
Clinical Trials
Clinical Trials
We conducted a Phase 1 Single Ascending Dose Study in Human Subjects at Stanford Medical Center
We tested the safety and tolerability in 13 healthy volunteers and 24 patients with cystic fibrosis (pwCF) on triple CFTR modulator therapy (Trikafta), as well as exploratory endpoints in pwCF.
Single ascending dose study with 4 dosing cohorts comparing formoterol alone or formoterol plus 3 doses of methacholine.
No adverse events or signs of intolerance were noted in both healthy volunteers and pwCF
No subjects met criteria for significant drop in lung function (FEV1), bronchial reactivity, or serious adverse event.
Despite the small sample size, positive trends for acute increases in lung function were noted.
Despite the small cohort and with a single treatment the improvement in mucus clearance is significant
Early human data (healthy volunteers and pwCF on Trikafta) supports safety of the approach
Early data from CF patients provides signal of improving lung function measures and mucus clearance
The company plans to conduct a phase 1, randomized placebo- controlled study in patients with non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis.
MCCSA2